A Dihybrid Cross Involves The Crossing Of Just One Trait. | A cross of parental types aabb and aabb can be represented with a punnett square: Basically, the idea is in monohybrid cross only one characteristic is the phenotypic ratio becomes 3:1. This video will show how to set up and solve everyone's favorite 16 square punnett square. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. We compare two different characteristics in a dihybrid cross.
In this cross the ratio would be as follows 3(tall purple): Using the probability method, calculate the likelihood of these phenotypes from each dihybrid cross: Since this is a dihybrid cross, the genotype for each parent is ssyy. Monohybrid cross deals with one genotypic traits whereas dihybrid cross deals with two traits crossed to see their possible genotype. How to complete a dihybrid cross.

The dihybrid cross problem can be a very challenging topic for ap® biology students to master. Dihybrid crosses reveal the law of independent assortment. Suppose that we would like to study the height trait as well as the seed color trait within the pea plants. Transcribed image text from this question. A cross of parental types aabb and aabb can be represented with a punnett square: Thus, a dihybrid cross involves two pairs of genes. Unlike a monohybrid cross, a dihybrid cross aims to study two different traits within an organism. In a dihybrid cross, aabb x aabb, what fraction of the offspring will be homozygous for both recessive traits? Dihybrid cross involves the inheritance of two pairs of contrasting characteristics (or contrasting traits) at the same time. • a dihybrid cross involves two traits. Dihybrid crosses — definition & examples. What is the percentage of the flowers being pink and short? It tells the outcome of just one trait.
A) a monohybrid cross involves a single parent, whereas a dihybrid cross involves two parents. When an organism is hybrid for a particular trait, but only one of two genes expresses itself and it is dominant over the other. Transcribed image text from this question. We compare two different characteristics in a dihybrid cross. Can you determine which statements are correct regarding a dihybrid cross between ssyy x ssyy?

Dihybrid cross is simply the cross between two pure species involving two pairs of gene. A dihybrid cross involves two traits. Basically, the idea is in monohybrid cross only one characteristic is the phenotypic ratio becomes 3:1. The f1 generation all purple). • the law of independent assortment states that allele pairs separate independently of each other during meiosis. To determine whether traits are inherited together or separately, gregor mendel crossed pea plants that differed in two traits. The dihybrid cross problem can be a very challenging topic for ap® biology students to master. This one character is responsible to bring about the change in specie. This video will show how to set up and solve everyone's favorite 16 square punnett square. This representation clearly organizes a… a. The same way as a regular cross, just with more boxes. • a dihybrid is an individual that is heterozygous at two genes (yyrr). 3 this is a test cross for height gene but not for colour gene.
Basically, the idea is in monohybrid cross only one characteristic is the phenotypic ratio becomes 3:1. The same way as a regular cross, just with more boxes. The two pairs of contrasting characteristics chosen by mendel were shape and colour of seeds: In this example, there are a variety of outcomes that may occur. Following a ssyy x ssyy cross, what fraction of the offspring are predicted to have a genotype that is heterozygous for both characteristics?
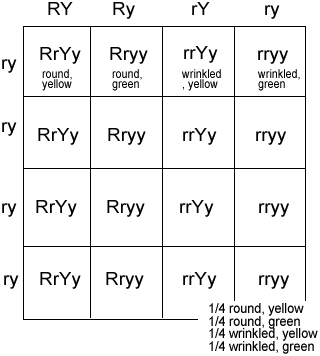
This law states that alleles are transmitted to offspring a dihybrid cross deals with differences in two traits, while a monohybrid cross is centered around a difference in one trait. Cross two homozygous plants ( rryy x rryy ) r = round seeds, r = wrinkled seeds y = yellow seeds, y = green seeds what percent will have cross a flower that is heterozygous for both traits with another flower that is pink and tall. We compare two different characteristics in a dihybrid cross. • a dihybrid is an individual that is heterozygous at two genes (yyrr). To demonstrate how this works, lets consider pea plants. Example solves a two trait (two factor) test cross which can then. This one character is responsible to bring about the change in specie. How to complete a dihybrid cross. • a dihybrid cross involves two traits. A) purple long and red long b) red vestigial and purple long c). Basically, the idea is in monohybrid cross only one characteristic is the phenotypic ratio becomes 3:1. The cross of these particular dihybrids produces four phenotypic classes. Recessive in the gene with alleles a and a from the cross.
A Dihybrid Cross Involves The Crossing Of Just One Trait.: Dihybrid crosses **crossing 2 different traits at the same time 1.